What is ACD?

An automated call distribution system, commonly known as Automatic Call Distributor (ACD), is a telecommunication system that answers incoming phone calls or video calls to distributes them within an organization. ACDs often provide some form of Automatic Customer/Caller Identification (ACIS), such as Direct Inward Dialing (DID), Dialed Number Identification Service (DNIS), Automatic Number Identification (ANI), or Video SPLIT ID (VSID) for use in routing calls based on a series of user-configured rules.
Its purpose is to help inbound contact centers sort and manage large volumes of calls or video calls to avoid overwhelming the team. It also improves customer experiences by making sure they are connected to a capable agent in the quickest time possible.
But before the caller is queued and routed, they first have to go through an IVR or RTC. IVR and RTC platforms are often confused each other with ACD, so let’s take the time to differentiate all these terms.
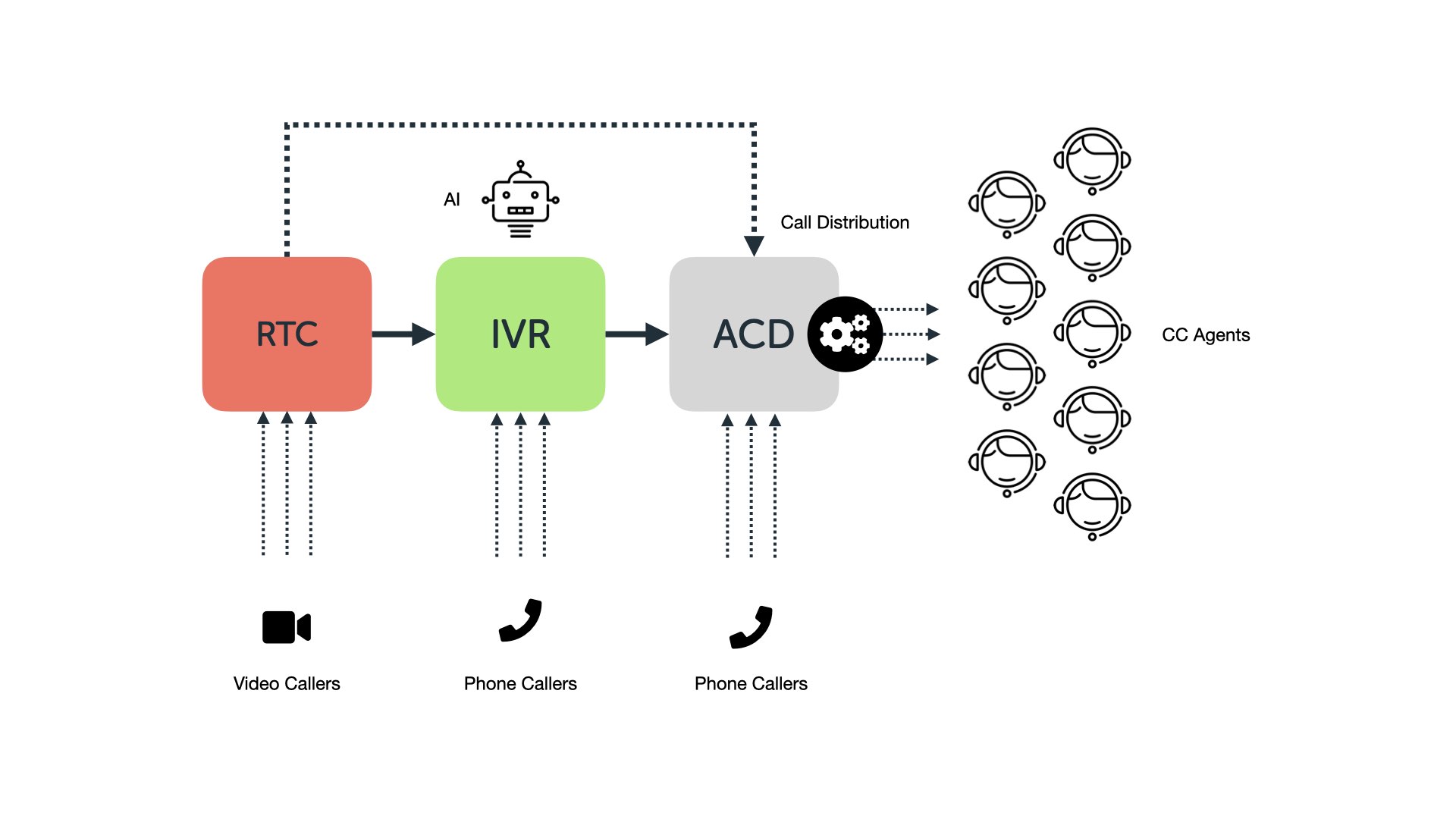
How does it works?
Call Identification
Caller ID systems can also be used to determine factors like language and location. This will allow the ACD to distribute the caller to an agent that’s best equipped to handle their concern.
Call Queueing
The next step is to sort the callers into a waiting list. The distribution system determines the order of the queue based on a number of factors such as: Status, Waiting Time, Query.
Call Routing
The last step is call routing. The ACD will route the calls based on your preferred type of distribution method. There are many types of distribution methods for you to choose from.
Most common Queue Distribution Methods…
◼️ Round Robin Call Distribution
A common distribution type for centers that want agents to have equal volumes of workload. In rotational distribution, agents all take turns in answering. For example, call 1 is taken by agent 1, call 2 is taken by agent 2, and so on. The cycle then repeats from the first agent once everyone has taken a turn.
◼️ Simultaneous Call Distribution
This is the preferred method if you want to reduce customer waiting time. With this routing strategy, the ACD alerts all agents to an incoming call at the same time. The first agent that picks up will handle the customer.
◼️ Random Call Distribution
This method is very simple if you have a lot of calls to handle that do not require specific skills. The next agent that picks up is a random selection of all agents available. After some time all agents will have the same number of calls in average without any specific condition.
◼️ Time Based Call Distribution
Time-based distribution takes into consideration your agents’ availability. The ACD will only alert agents that are available and will send the call directly to voicemail if none are open to handling it. If your call center prefers not to take calls during off-hours then this is a good choice.
◼️ Talk Time Based Distribution
Similar to rotation, talk-time distribution tries to divide workload fairly among your agents. Here, the ACD selects the agent with the least talk-time and gives them the next ticket in the queue. This balances the workload between the team by making sure each agent has worked an equal amount of time.
Interactive Powers - Streamline your business communications